Treating solid waste in urban sewage usually involves the following steps and considerations:
Pretreatment:
Screening and sand removal: Remove large particles and grit through screening nets and settling tanks to prevent them from entering the solid-liquid separator and reduce the risk of equipment wear and clogging.
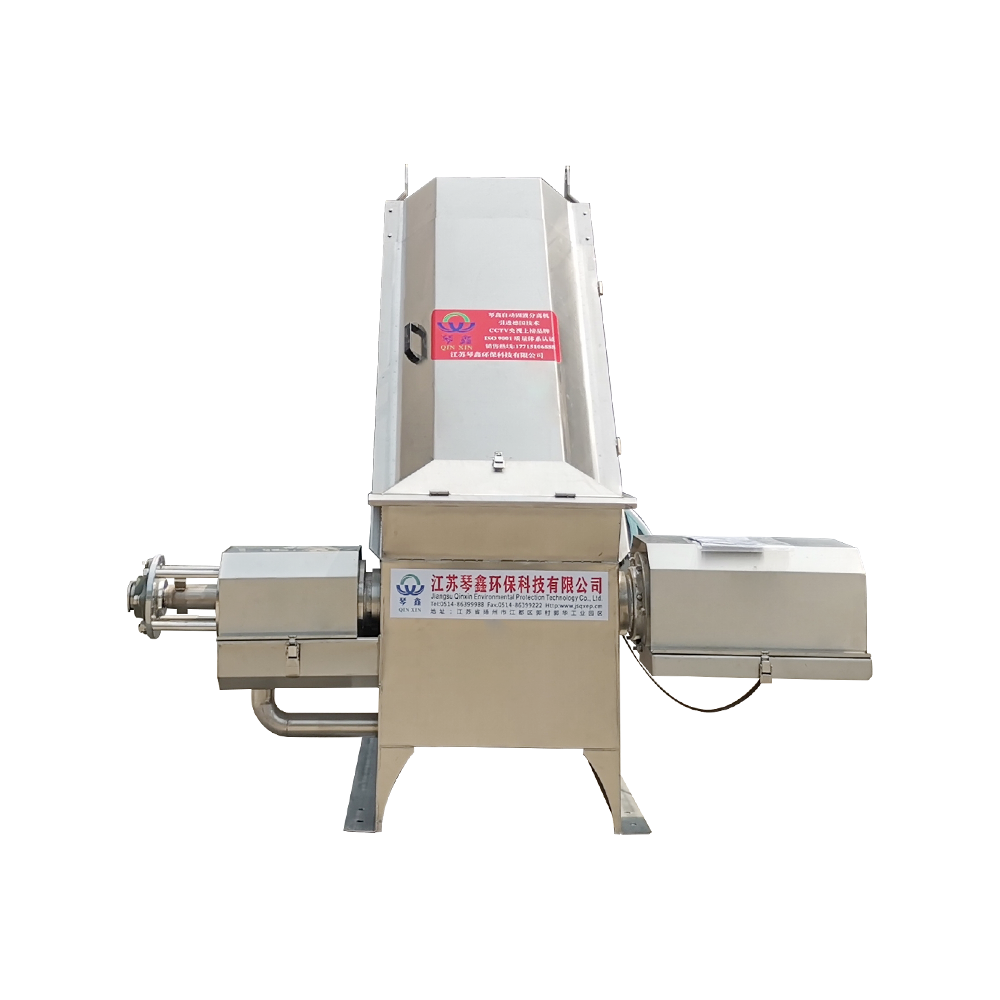
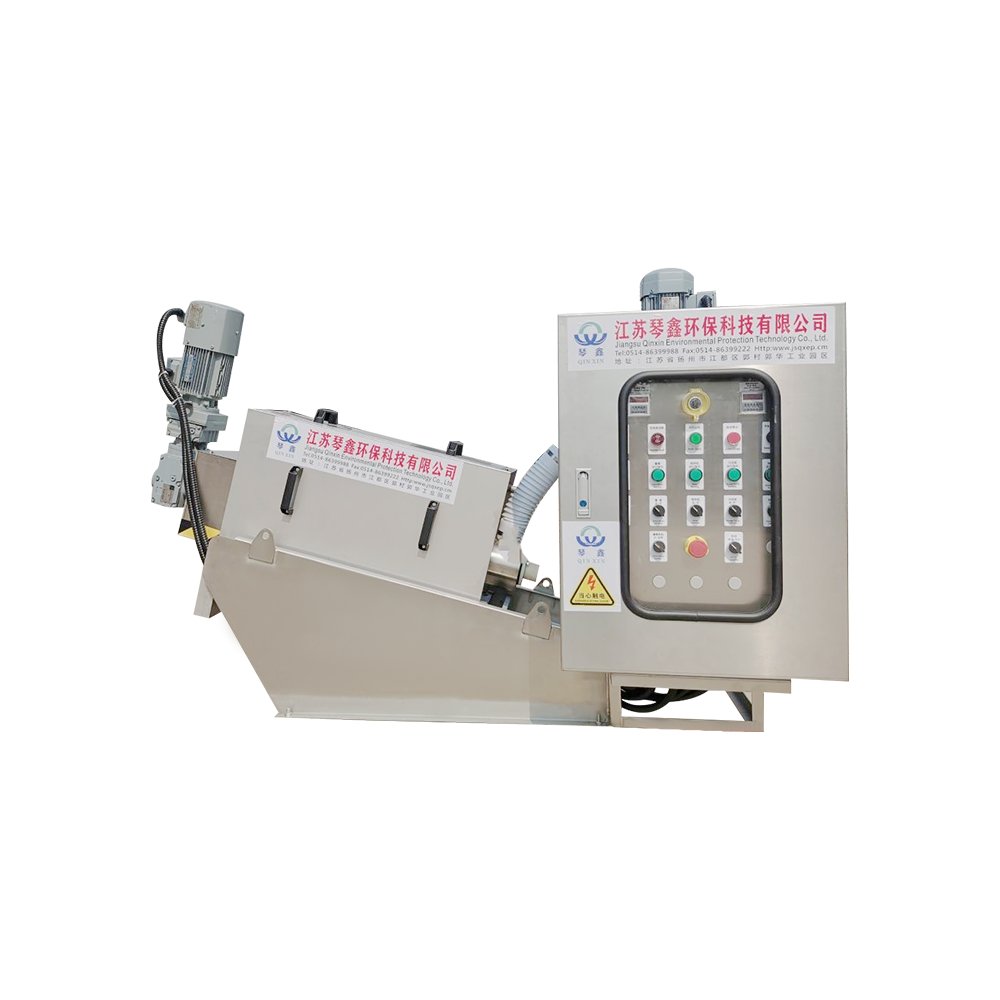
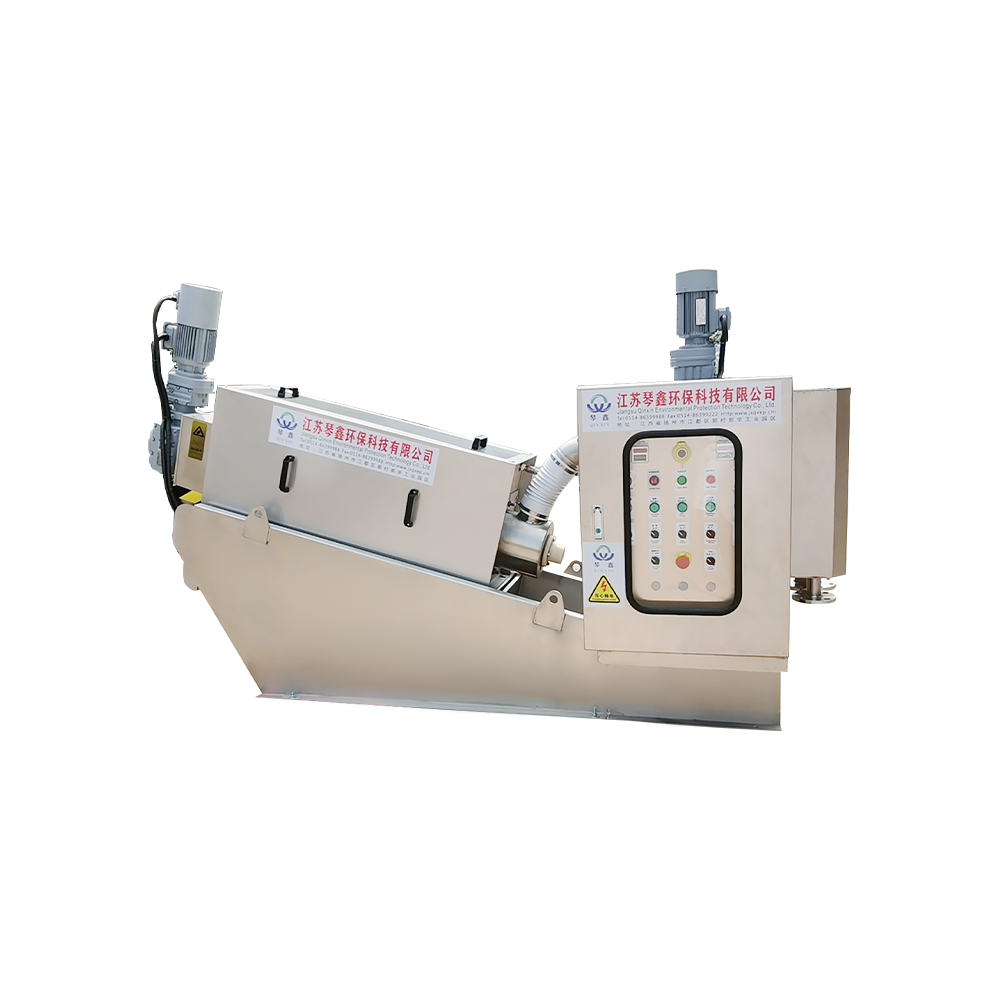
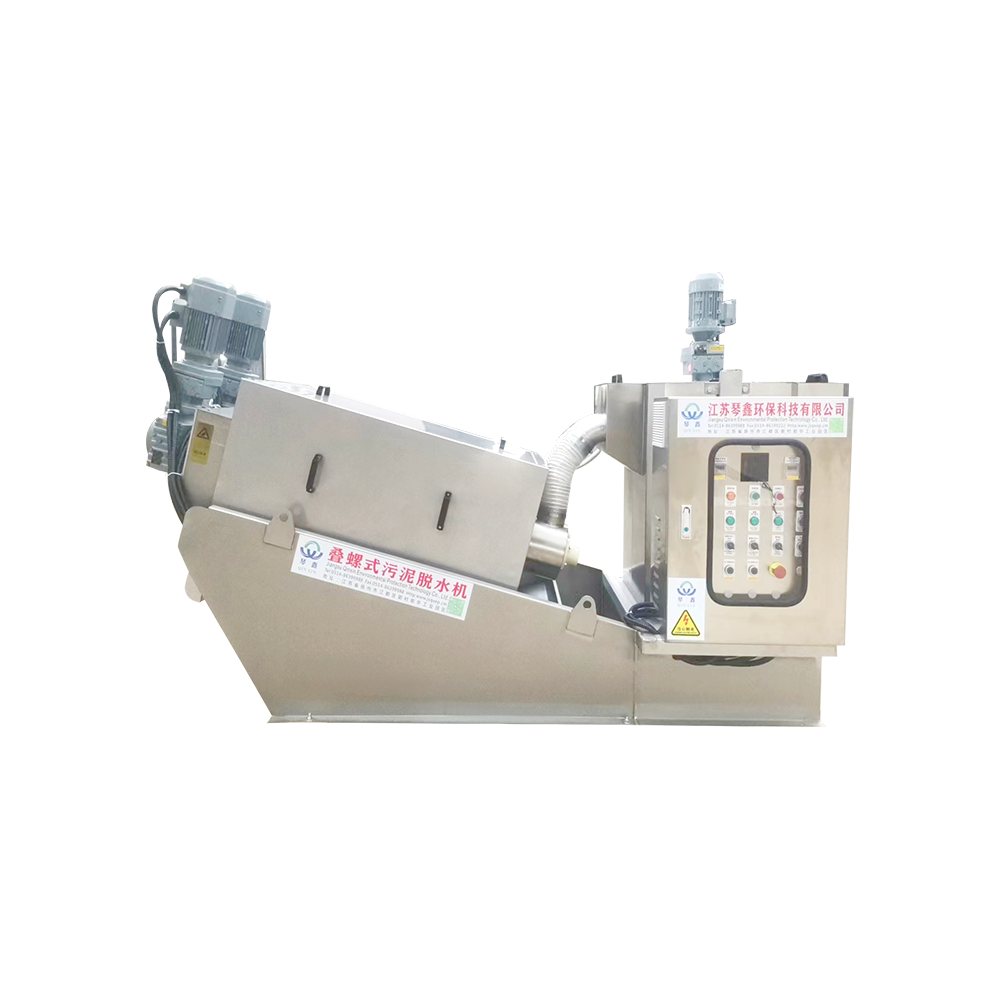
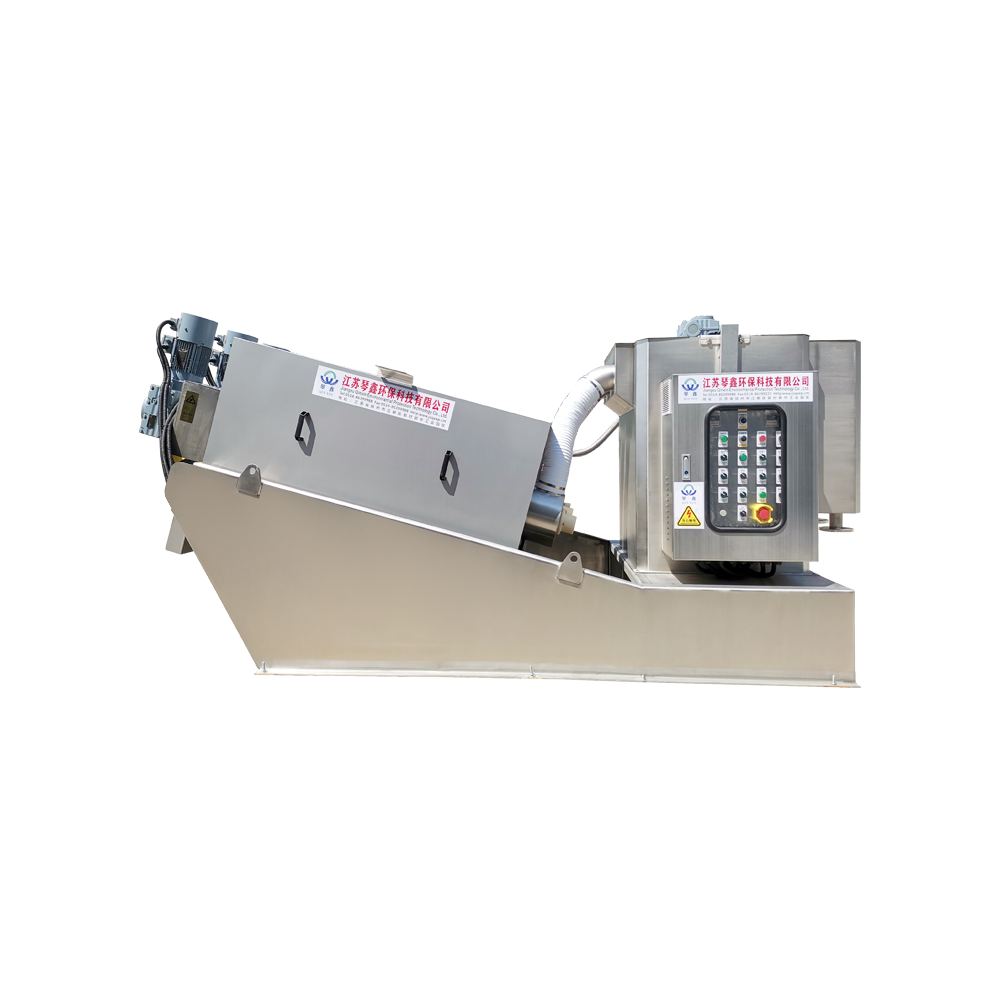
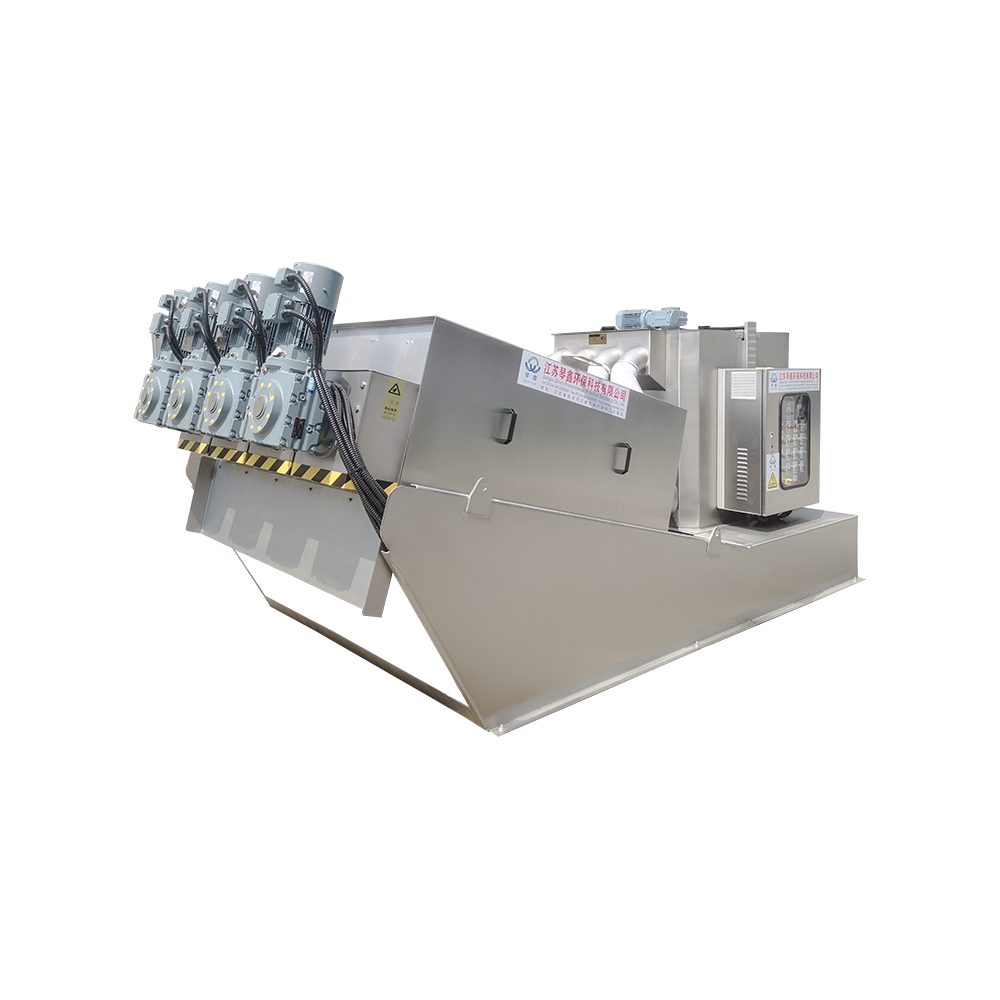
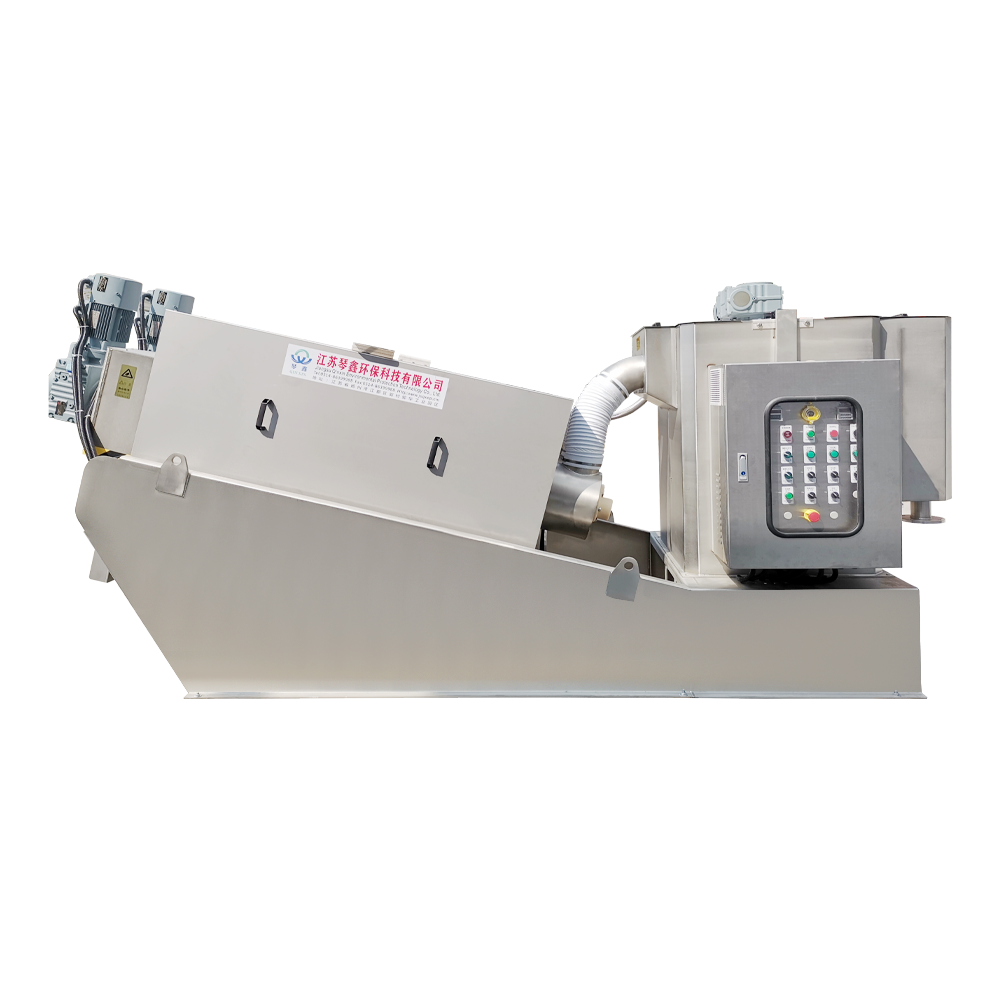
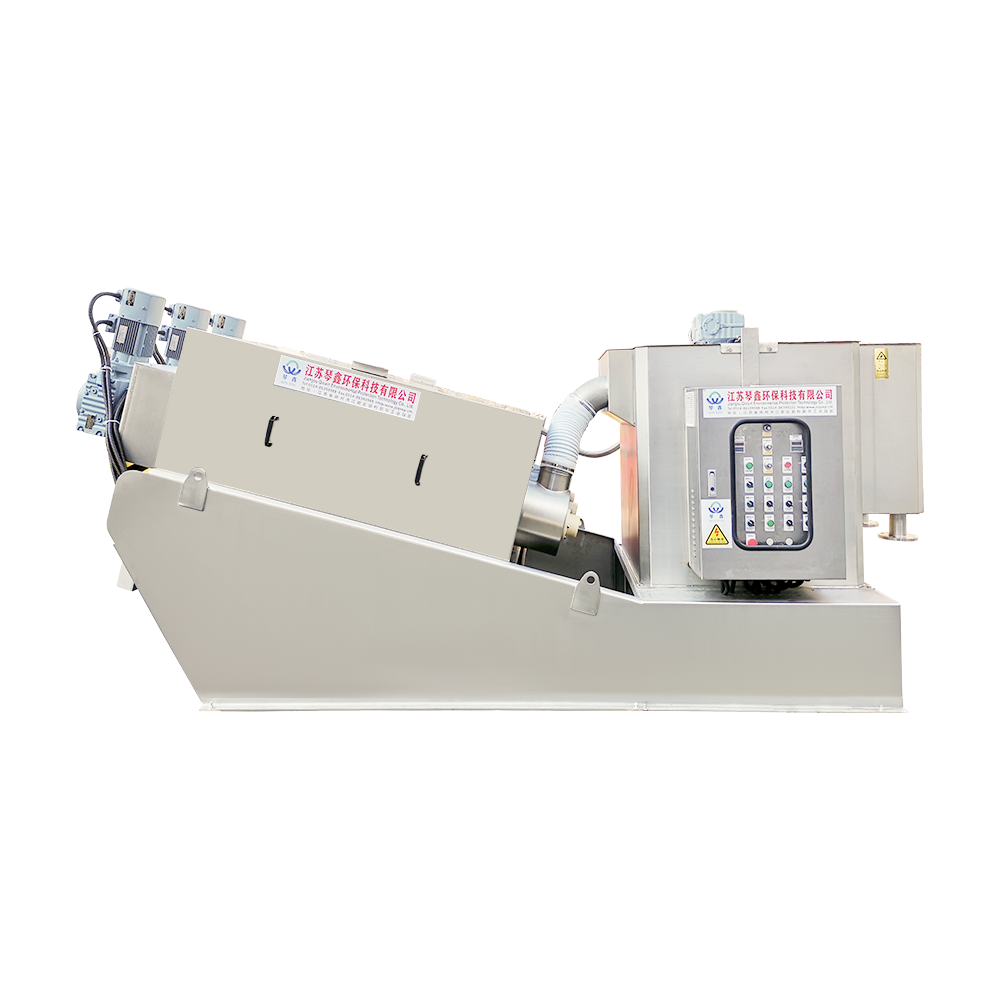
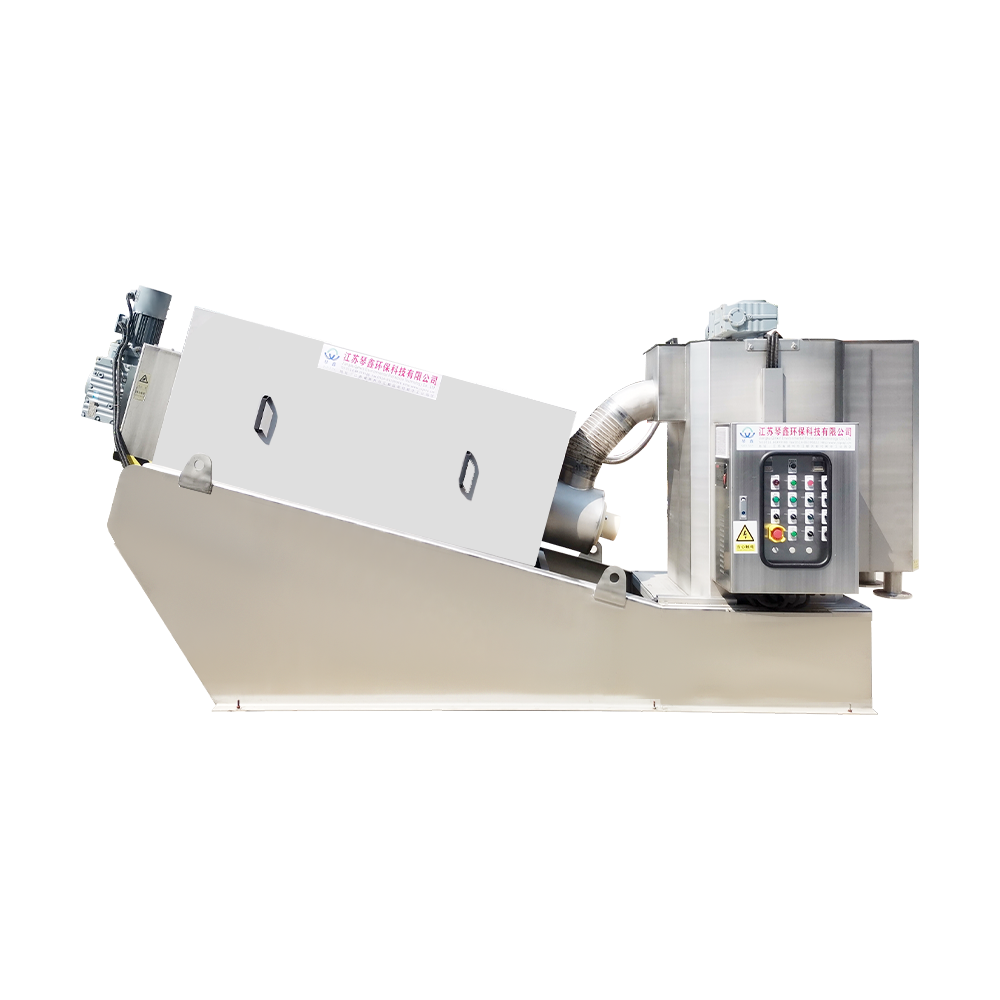
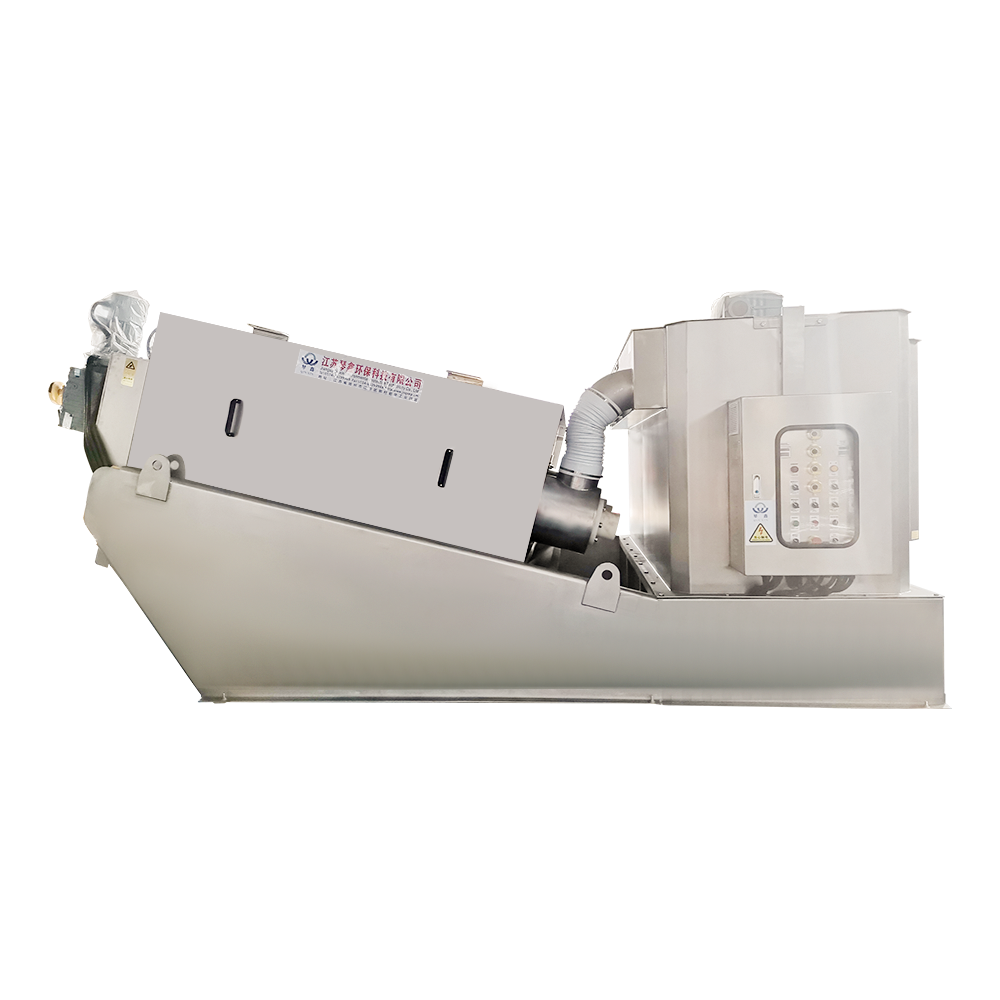
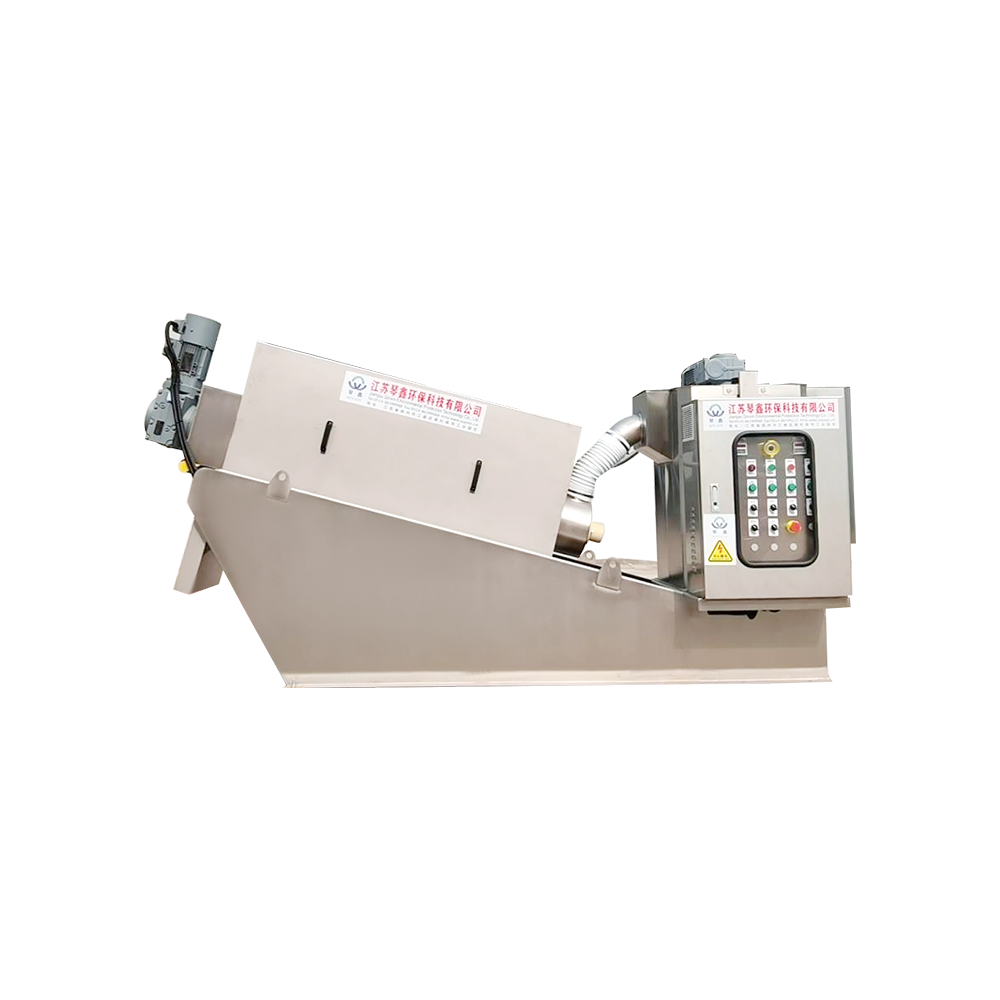
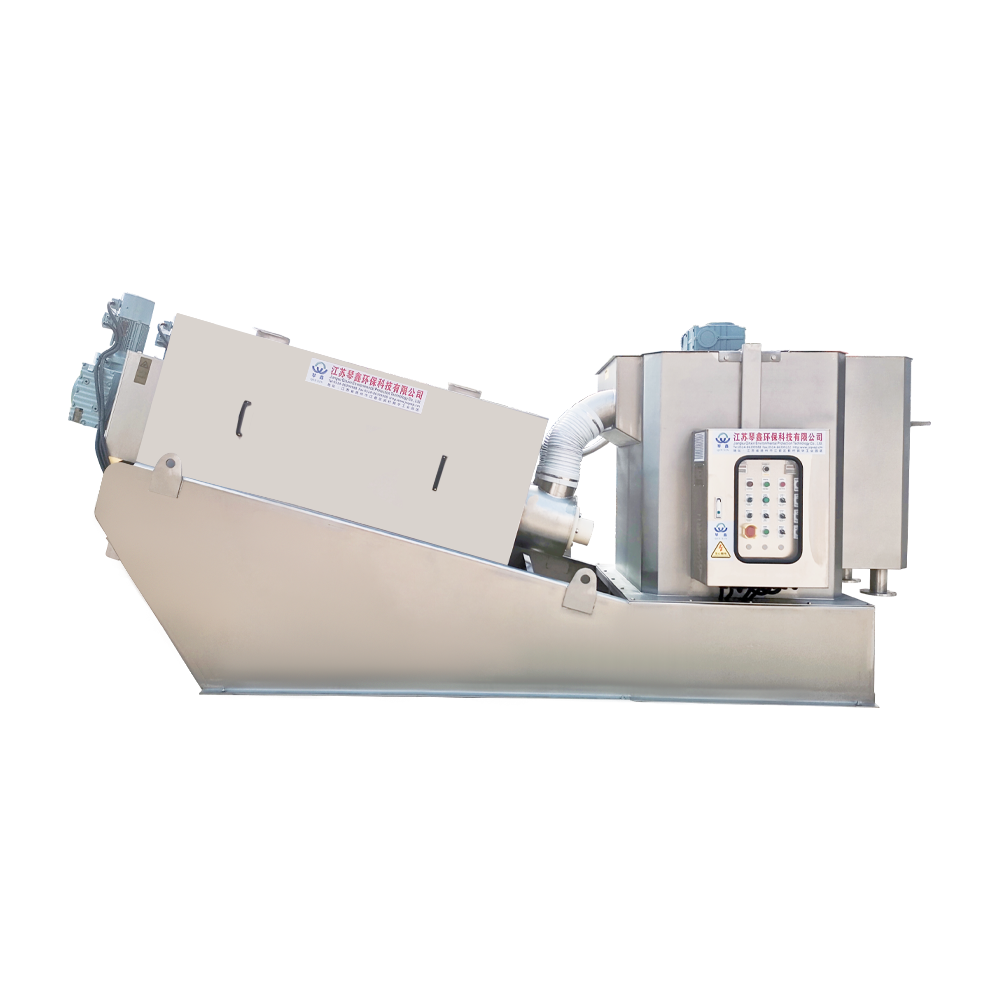
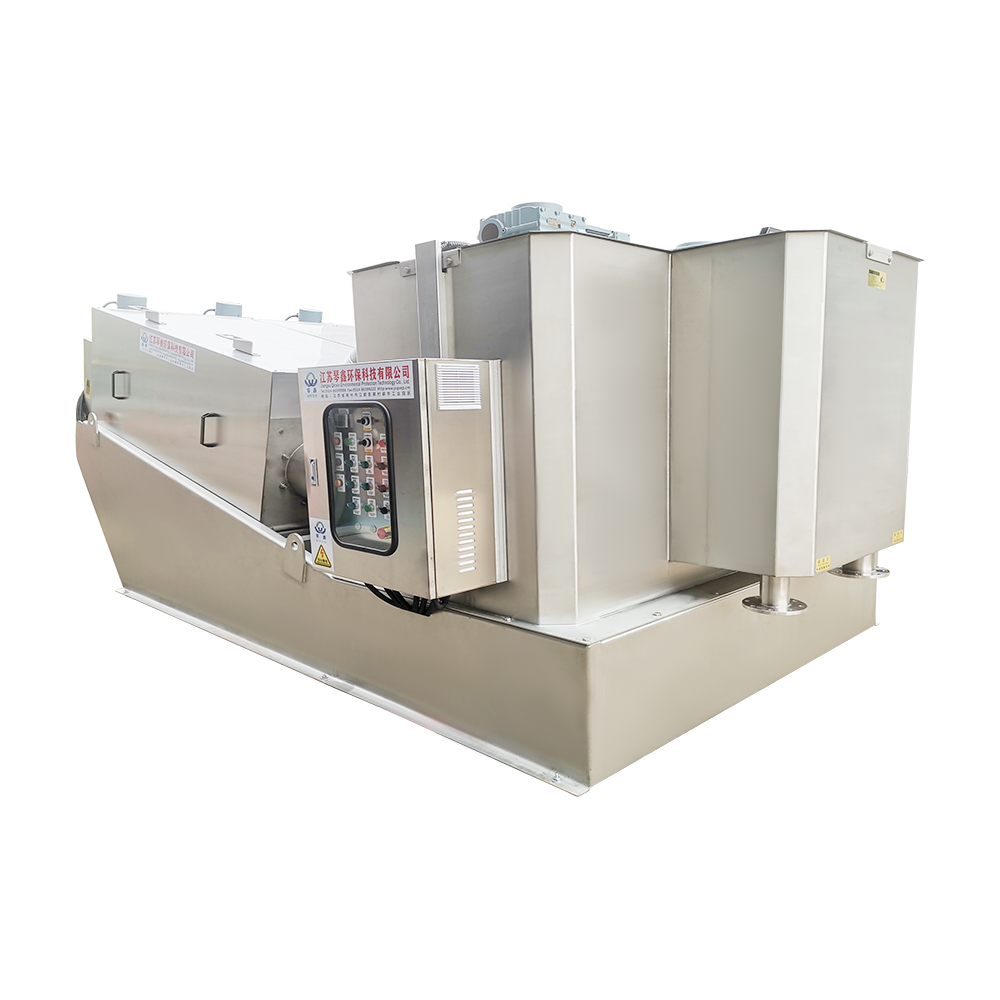
Selection of solid-liquid separator:
Centrifugal separator: Suitable for treating sewage containing larger solid particles, separating solids through centrifugal force.
Filter: It has a better separation effect on fine particles or colloidal substances. Different levels of filters can be selected to treat solid wastes of different sizes and properties.
Operation optimization:
Adjust operating parameters: such as speed, feed concentration, cleaning cycle, etc. to maximize separation efficiency and equipment life.
Regular maintenance: Keep the equipment clean and in good operating condition, and regularly clean the screen holes and internal components of the filter or centrifugal separator to prevent clogging and performance degradation.
Treated solid waste:
Disposal and recycling: Treated solid waste may require further treatment or recycling, such as compaction, incineration or landfill.
Monitoring and improvement:
Monitoring water quality: Regularly test the quality of treated sewage to ensure that the effect of the solid-liquid separator meets environmental protection requirements.
Improving technology: Continuously optimize the selection and operation methods of the solid-liquid separator according to actual conditions and treatment effects.
Through the above steps and strategies, the solid-liquid separator can be effectively used to treat solid waste in urban sewage, meet environmental emission standards and achieve effective utilization of resources.

 ENG
ENG
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt ไทย
ไทย











 TOP
TOP